
Companies sometimes measure the accounts payable turnover ratio by only using the cost of goods sold in the numerator. This is incorrect, since there may be a large amount of administrative expenses that should also be included in the numerator. If a company only uses the cost of goods sold in the numerator, this creates an excessively high turnover ratio. For instance, in the case of a 10/30 credit term, as a buyer, you might benefit from a 10 percent discount, granted that the balance is paid within 30 days. In general, the standard credit term is 0/90 – which facilitates payment in 90 days, yet no discounts whatsoever. When beginning to calculate APP for businesses it is important to consider the number of days within the period.
Key Takeaways
However, there are certain drawbacks of the average payment period, like it does not consider qualitative aspects of the relations with the suppliers. For instance, if monthly credit purchase amounts to $30,000, it needs to be divided by 30, and per day credit purchase amounts to $1,000 ($30,000/30). Typically, the businesses use the yearly payable period, and the amount for credit purchase needs to be divided by 365.
Points to Remember While Calculating Average Payment Period
Days Payable Outstanding is a key financial metric that measures the average number of days a business takes to pay its suppliers and vendors for goods and services received. When a company takes too long to collect outstanding accounts receivable, has too much inventory, or pays its expenses too quickly, it lengthens the CCC. When a company collects payments quickly, correctly forecasts inventory needs, or pays its bills slowly, it shortens the CCC. If two companies have similar values for return on equity (ROE) and return on assets (ROA), investors may choose the company with the lowest CCC value. It can set stricter credit terms limiting the number of days an invoice is allowed to be outstanding.
- This includes any discounts awarded to customers, product recalls or returns, or items re-issued under warranty.
- This article will focus on measures of financial performance and will detail the skills and knowledge expected from candidates in the FMA/MA exam.
- A high DPO can be a can be a positive sign that a company is using its capital resourcefully, but if it’s too high, it may be struggling to make payments.
- Cash isn’t a factor until the company pays the accounts payable and collects the accounts receivable.
- Of course, unmet invoices must eventually be taken care of by the company, but the company is free to spend that cash in the meantime for other needs.
- We believe that sustainable investing is not just an important climate solution, but a smart way to invest.
Days Payable Outstanding FAQs
For example, an average collection period of 25 days isn’t as concerning if invoices are issued with a net 30 due date. However, an ongoing evaluation of the outstanding collection period directly affects the organization’s cash flows. When analyzing average collection period, be mindful of the seasonality of the accounts receivable balances. For example, analyzing a peak month to a slow month by result in a very inconsistent average accounts receivable balance that may skew the calculated amount. The average collection period is an accounting metric used to represent the average number of days between a credit sale date and the date when the purchaser remits payment. A company’s average collection period is indicative of the effectiveness of its AR management practices.
When the turnover ratio is increasing, the company is paying off suppliers at a faster rate than in previous periods. An increasing ratio means the company has plenty of cash available to pay off its short-term debt in a timely manner. For instance, if the balance is paid by the due date specified by the supplier, a business may receive a 10% discount on its purchases from the supplier. Suppliers are more likely to provide special payment rates if the company’s APP demonstrates that it is capable of quickly paying off its credit balances and covering its immediate expenses.
Low DPO
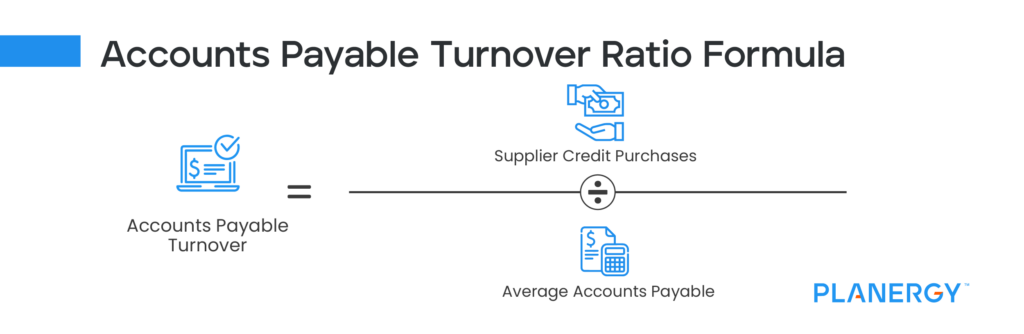
By evaluating its DPO, it can project its creditworthiness, liquidity, and financial health. When a company’s DPO is high, this may either mean the company is struggling to pay bills on time or is effectively using credit us tax deadlines for expats businesses 2021 updated terms. The equation to compute the average accounts payable of a company is as follows. Let’s analyze the concept from suppliers’ perspective as they are primary stakeholders in the average payment period of the business.
Offering incentives for early payments and implementing masterful collection strategies can significantly enhance the performance ratio and, consequently, your average payment period. It looks at how many times a company’s operating profits exceed its interest payable. The higher the figure, the more likely a company is to be able to meet its interest payments.
For instance, when considering a quarterly report the number of days will vary even if you are considering annual financial statements. Advisory services provided by Carbon Collective Investment LLC (“Carbon Collective”), an SEC-registered investment adviser. StockMaster is here to help you understand investing and personal finance, so you can learn how to invest, start a business, and make money online. If the payment terms are set at 30 days, then 38 days is probably too long to settle payment and may potentially be causing some consternation to your suppliers. While DPO measures how long it takes to pay suppliers, Days Sales Outstanding (DSO) measures how quickly your company collects payments from customers.
No Comments